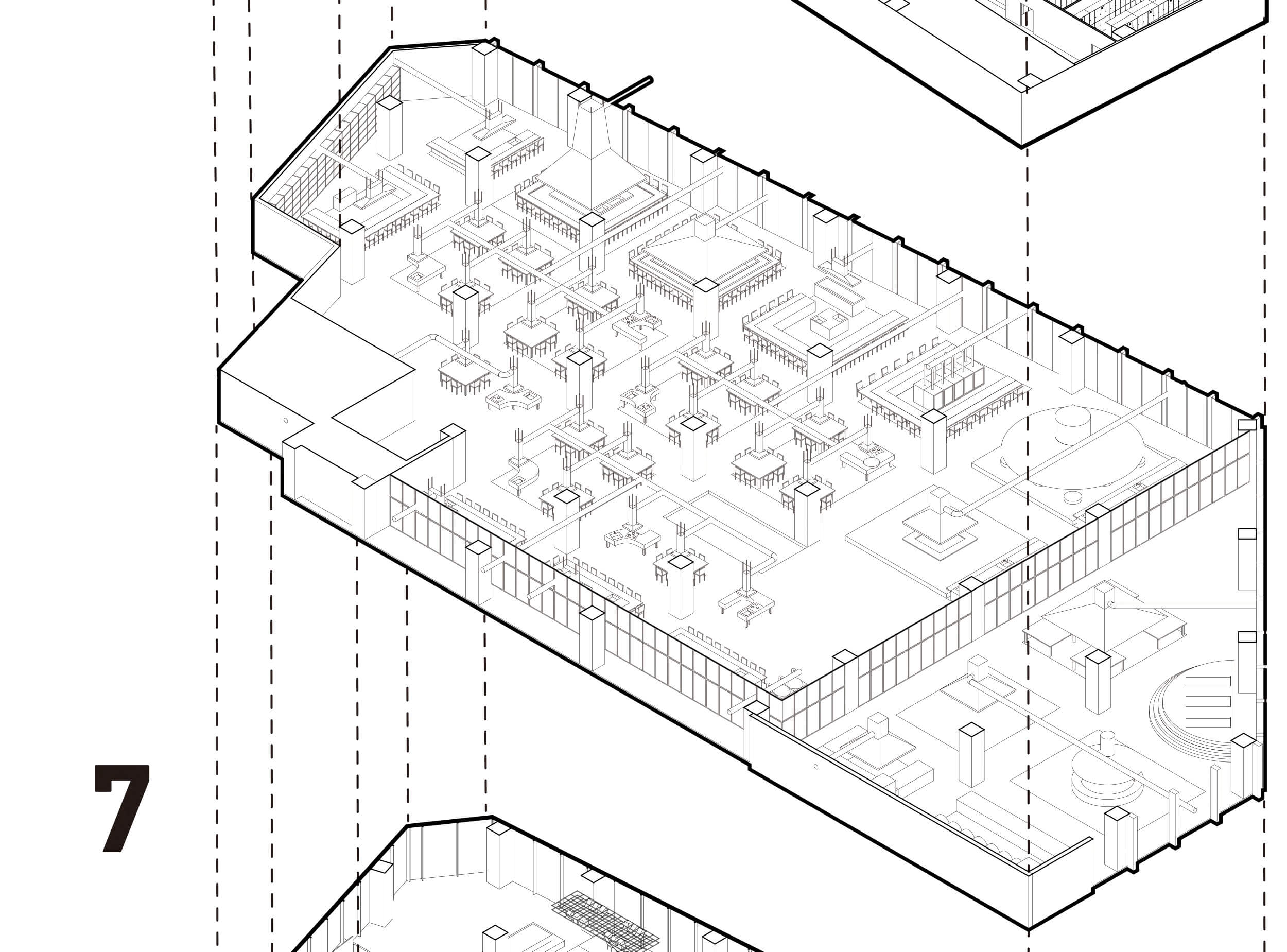
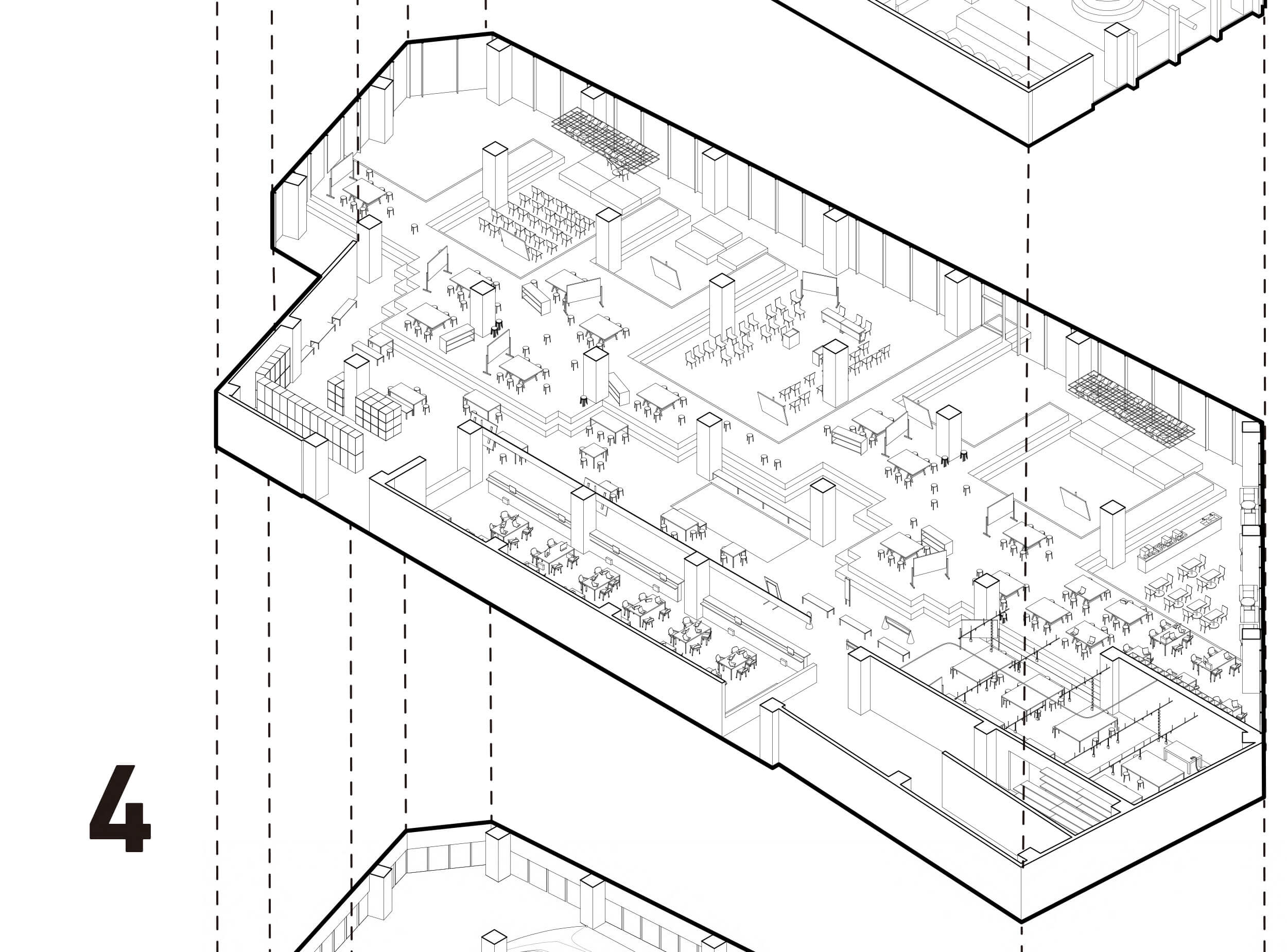
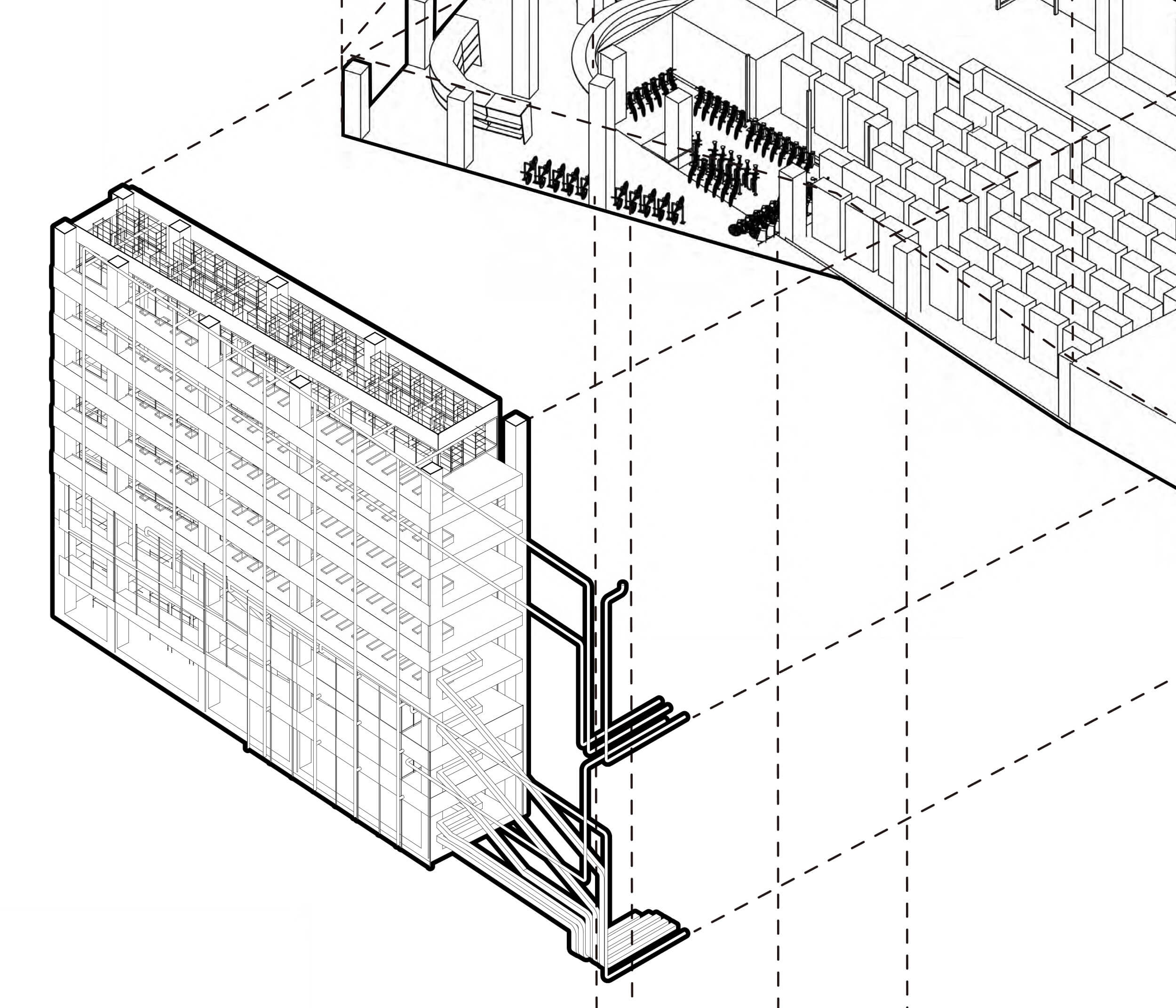
The fashion industry affects the environment at every stage, for example, the procurement of raw materials to the production, transportation, and disposal of fab- rics and garments. Garments are made from a mixture of materials, and are produced in a number of factories and companies overseas. As a result, it is difficult to grasp the actual status and full extent of environmental impact. While the number of garments supplied in Ja- pan is increasing, the price per garment is getting low- er every year, and the market size is decreasing. Mass production and mass consumption are expanding, and the life cycle of clothing is becoming shorter. The trend toward mass disposal is accelerating. This is one of the reasons why the fashion industry has such a large im- pact on the environment. In fact, the average annu- al clothing consumption per person today is about 18 pieces of clothing purchased, 12 pieces of clothing giv- en away, and 25 pieces of clothing not worn. This means that there are a lot of clothes that are produced and pur- chased, but not worn and thrown away.
Ikebukuro is a place where department stores such as Seibu and other shopping facilities such as Sunshine City are concentrated. A wide range of clothes are sold there, from luxury brands to fast fashion, and many people come to Ikebukuro to buy clothes. Many people visit Ikebukuro to buy clothes. In such places, fashions go out of style quickly, and you can see big red letters saying “Sale” at the entrance of stores everywhere. These signs entice consumers to buy. But even then, the unsold items are not recycled, but discarded.
Planned obsolescence is one of the ways to stimulate consumers to buy and consume. It is a method to make consumers buy new products by designing them in ad- vance so that their quality will intentionally deteriorate during use. In addition, short warranty periods and high repair costs also encourage consumers to buy. The system of mass production and the strategies of these companies continue to incentivize consumers to buy. It has become normal for consumers to live in a cycle of buying new things and then throwing them away. They have formed an easy way of thinking that if they find a slight defect, it is time to replace it.
Modern people today prefer to buy new products that are free of defects. But Naples refuses to do that. For ex- ample, when a car breaks down, it is repaired using a wooden stick found in the street. That repair is tempo- rary, so they will repeat repairs and breakdowns. In oth- er words, they believe that objects are made up of a cy- cle of breakdown and repair. It is through the repair of broken objects that we can understand the mechanisms of objects. Modern people have forgotten this fact.
All objects fall apart and break down as we use them. As we repeatedly repair and rebuild them, we gradual- ly become attached to them. Attachment is the act of using something as long as it does not lose its function due to damage or breakage. In this way, the damaged part of a piece of metalwork is reevaluated as a value, and it is transformed into an attachment. We believe that clothes can be treated in the same way. Observe the flaws in the clothes and give them the appropriate treatment. This may be a time-consuming process, but it may allow us to continue using the clothes for a long time with affection.
PHILOSOPHY OF DECOMPOSITION (2019)
Fujiwara Tatsushi
The world we live in is filled with abundance between new products and waste, production and products, life and death for example grbage that transforms into toys, robots that return to the earth, whales that are buried, invisible microorganisms and so on. This book exam- ines the possibilities of “disassembly,” which is now talked about even more negatively, in various fields such as pedagogy, robotics, scrap pickup, ecology, and the world of repair.